Manage organisational data
Manage your organisation's master data with the Robin Data ComplianceOS®. Access identical data across all functions and areas that precisely matches your organisation.
Content
Background
The organisation master data in Robin Data denotes relevant basic data (such as assets, content groups, affected groups, functional areas, etc.) that can be considered relatively constant over a period of time. This data is an important component to capture processing of the organisation in Robin Data.
For efficient management of master data, Robin Data has an area called "Organisational Data". By maintaining organisation master data, you can access identical data across all functions and areas in Robin Data ComplianceOS® that precisely matches your organisation. Inefficient structures due to individual data silos and deviations to your organisation are thereby avoided.
Open organisational data
The organisational data can be found in the main navigation bar on the right side next to the name of your organisation. The menu item organisational data is marked with the icon ![]() .
.
Click to enlarge image.
- In the main menu click on the icon
 : A dropdown menu opens.
: A dropdown menu opens. - Move the mouse pointer over the desired menu item in the dropdown menu: Another dropdown menu opens.
- Click on the desired area in the second dropdown menu: The selected organisational data area opens.
Individual areas of organisation master data
The menu area of the organisational master data is divided into four sections:
Organisation
In the area Organisation you can define your organisational structure. You can retrieve the data entered here in the respective area in the documents.
For example, the locations and functional areas can be selected in the documents in the Governance tab and thus an assignment of the documents can be made. In addition, you can define an authorisation concept on this assignment.

Locations
Under the organisational data, locations of the organisation can be created. Larger organisations such as groups of companies, corporations, municipal administrations or social welfare organisations often consist of several sites between which personal data is transferred. From a data protection perspective, it is important to ensure that the transfer between these sites is legally permissible.
For detailed instruction on how to manage locations, see the article Manage locations.
Persons
Under the organisational data, persons of the organisation can be imported or created. The most important part of an organisation is its employees. In Robin Data ComplianceOS® you can enter these employees as persons, assign them to specific locations, and assign their function within the organisation.
For detailed instruction on how to manage persons, see the article Manage persons of your organisation.
Functional areas
Under organisational data, organisation-internal functional areas can be imported or created. Functional areas are used to delimit task areas of functional organisations from each other. Robin Data provides users with common functional areas, these can be imported into the account. In addition, other functional areas can be created. Examples of functional areas are accounting, purchasing or human resources.
Functional areas can be selected whenever users create people in the Robin Data ComplianceOS®. For example, when creating people at locations or external contacts.
For detailed instruction on how to manage functional areas, see the article Define functional areas.
Roles
Under Organisational data, internal organisational roles can be imported or created. In contrast to functional areas, roles do not refer to task areas that combine different roles in the organisation (e.g. accounting), but to individual cross-area roles (e.g. area manager). Robin Data provides users with common roles, these can be imported into the account. Additional roles can be created. Example roles are department manager, data protection coordinator or authorised signatory.
Roles can be selected when users create people at the sites in Robin Data ComplianceOS®.
For detailed instructions on how to manage roles in the organisation, see the help article Manage roles in the organisation.
Recipient
Under Organisational data, recipients can be imported or created. Recipients refer to certain categories of people within your organisation. Robin Data provides users with common recipient groups, these can be imported into the account. In addition, other recipients can be created. Exemplary recipients are employees, shareholders or employees of the human resources department.
Recipients play a role especially when you want to analyze where data flows to. The internal recipients created in this area of the organisational data can be stored when creating processing activities.
For detailed instruction on how to manage recipients, see the help article Define recipients.
Data subject groups
Under Organisational data, data subject groups can be imported or created. Affected groups combine different new or existing elements in Robin Data. Depending on the organisation, creating a concern group for applicants, employees or customers can be useful. This eliminates the need to add each person individually to a record. For example, data subject groups can be easily added when creating processing activities.
For detailed instructions on how to manage data subject groups, see the help article Define data subject groups.
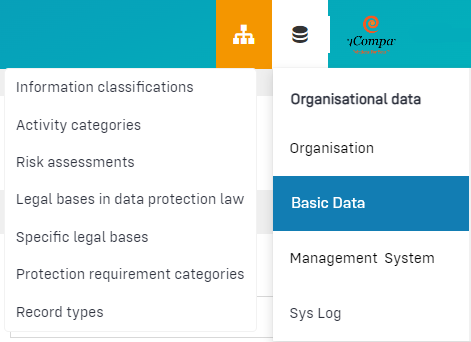
Basic Data
In the basic data you can make basic configurations for your client.
Information classifications (formerly documented information)
Under Organisational data, information classifications can be imported or created. Information classifications summarises categories of documents in Robin Data and supports the effectiveness of an organisation's quality management system. Robin Data provides users with common information classifications, this can be imported into the account. In addition, otherinformation classifications can be created. Examples of information classifications are work instructions, ISO documents or guidelines.
Information classifications must always and at any time be identifiable and clearly assignable. For this reason, information classifications have a unique identifier, a so-called document ID. Relevant documents are provided with a document ID in the Robin Data ComplianceOS®.
For detailed instruction on how to manage information classifications, see the help article Information classifications and document IDs.
Activity categories
Under Organisational data, activity categories can be imported or created. Activities can be categorised, some of which are derived from data protection law (e.g., data subject rights) or arise from day-to-day data protection work (e.g., planned data deletions). Robin Data provides users with common categories of activities, these can be imported into the account. In addition, other categories can be created. Example categories of activities are request from a data subject, document review or implementation of an erasure rule.
These and other activity categories can be selected in the Robin Data ComplianceOS® when entering an activity. All activities then flow into an activity report, which, for example, provides evidence of the annual activities in data protection at the end of the year.
For detailed instruction on how to manage activity types, see the help article Define activity categories.
Threshold risks (processing activity)
Classes for threshold risks can be imported or created under organisational data. The classification of threshold risks is used to categorise the possible risks for the data subjects arising from a processing activity. To assess the risk, a threshold analysis is first performed and the risk is finally classified using the created threshold risk classes.
Robin Data provides users with common classes for threshold risks. These can be imported into the account. In addition, further classes can be created. The classifications from 0 "No identified risk present" to 5 "Very high" have been established for threshold risk analyses.
The risk assessment plays a role when you create processing activities.
For detailed instructions on how to manage roles in the organisation, see the help article Define the risk assessment.
Legal bases in data protection law
Under Organisational data, legal bases in data protection law can be created. Robin Data provides users with the most important legal bases in data protection, such as common state data protection laws, but also specific data protection laws of the federal states or the Catholic and Protestant churches. In addition, further legal bases in data protection can be created. Exemplary legal bases in data protection are the individual articles of GDPR or BDSG.
Legal bases in data protection play a role when you create processing activities, among other things.
For detailed instruction on how to manage the legal basis in data protection law, see the help article Manage data protection legal bases.
Specific legal bases
Under Organisational data, specific legal bases can be created. Robin Data provides users with the most important special legal bases. Whenever data protection law also affects other legal bases, it is recommended to document them. As an example, one can consider the legal obligation to transmit wage data to the tax office. In addition, other special legal bases can be created. Examples of special legal bases are the Commercial Code, the German Infection Protection Act or the Trade Regulation Act.
Special legal bases play a role when you create processing activities.
For detailed instructions on how to manage special legal bases, see the help article Manage special legal bases.
Protection requirements (governance tab)
The protection requirement can be imported or created under organisational data. The protection requirement defines the required level of protection for data in a specific situation in order to prevent damage. Robin Data provides users with common protection needs from DIN 66398, these can be imported into the account. In addition, further protection requirements can be created. Exemplary protection requirements are the protection classes 1 to 3, the security levels 1 to 7 or the confidentiality levels "public data" to "top secret data".
The protection needs are used when creating documents in the Robin Data ComplianceOS® and are maintained via the Governance tab.
For detailed instruction on how to manage the protection requirement, see the help article Define protection requirement.
Record types (formerly contract type)
Under Organisational data, record types can be created. Contracts can be divided into categories or types, some of which are derived from data protection law (e.g. order processing contract). Robin Data provides users with common record types, these can be imported into the account. In addition, further record types can be created. Example record types are the attorney contract, license contract or the jointly responsible party contract.
These contract types can be selected in the Robin Data ComplianceOS® when entering contracts with external contacts.
For detailed instruction on how to manage contract types, see the help article Define record types.
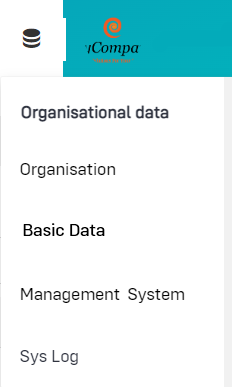
Management System
The area Management System allows you to configure the basic parameters of your management strategy. For example, you can structure your assets and risks or store your own valuation schemas via the content groups.
Content groups
Under organisational data, content groups can be defined. Content groups combine different new or existing elements in Robin Data. For example, users could define a content group for all locations. This eliminates the need to add all locations individually to a record. Currently, the application of content groups is possible in the "Governance Tab" under the "Governance Tag" section.
For detailed instruction on how to manage content groups, see the help article Define content groups.
Asset classes
Under organisational data, asset classes can be defined for your organisation. Classification is used to subject assets in a class to the same assessment scheme at all times, ensuring consistent protection needs analysis across all assets in a class and over time.
Assets consist of a category or main category and multiple classes or subclasses. First, the asset subclasses must be created so that they can be selected for the asset classes.
Risk fields
Under organisational data, you can define risk fields for your organisation. Structuring serves to always subject risks of a field to the same evaluation scheme and thus to ensure consistent risk analysis across all risks of a risk field and over time.
Risks consist of a field or main category and several categories or subcategories. First, the risk fields must be created so that they can be selected for the risk categories.
Programmes and Controls (import)
Under organisational data, you can import programs and controls (i.e. standards) relevant to your licensed compliance fields as controls and assign each to a maturity model.
Audit types
Under organisational data, you can configure which types of audits you have. These audit types can be used in the Programs > Audit.
System Log
Under organisational data, you can view the system log files of the software of your account. You can see which user made which changes and when.
Further questions? - We are here for you.
If you have any questions about the software, please contact our support team. You can reach us at support@robin-data.io.