Manage the record of proccessing activities
The record of processing activites is the central document for demonstrating data protection in an organisation. It is therefore mandatory for any type of organisation. It is expedient to keep this record digitally.
Content
Background
According to Art. 30 of the GDPR, every organisation is required to maintain a record of processing activities. In everyday use, it is also referred to as a "records of processing".
In the records of processing activities all processes of the organisation in which personal data are processed are analysed. How detailed this analysis is carried out depends on the process and the risks involved in processing the person data.
Therefore, processes also summarise individual detailed processes in a larger context. For example, "applicant management" is often not subdivided into the sub-processes:
- Receipt of the application
- Processing of the application
- Distribution of the application
- Failure of the applicant
- etc.
They are instead based on the definition of the processes,
- Which personal data (so-called "data categories")
- For which purpose (e.g. "implementation of an application procedure")
- On which legal basis (here: consent of the applicant, initiation of an employment contract and legitimate interest of the employer)
- How it is processed (here: by e-mail, by file server)
- Who receives this data (here: HR department, relevant specialist department, management)
By considering these and other aspects, it becomes clear to the processor of such a process whether the processing is lawful and appropriate, whether there are risks for the data subjects, and perhaps also at which point such a process, or its sub-processes can be optimised.
Furthermore, the directory of processing activities provides a good overview of which IT systems or documents are used in the organisation to process personal data.
This question is important in order to clarify whether a so-called processor has been involved in the processing. Special contractual arrangements would then have to be made with this processor.
For more information on the record of processing activities, see our wiki article on the subject.
Manage the record of processing activities
- In the main menu click on Data protection: A dropdown menu opens.
- In the dropdown menu click on List of processing activities: The table view opens.
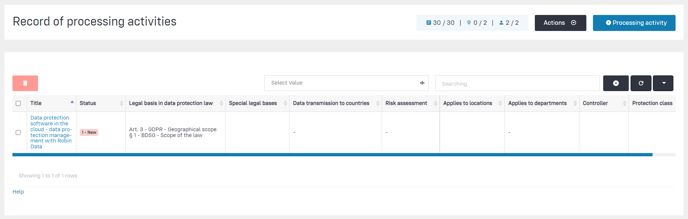
The general functionality of the table view is described in the article Using the table view. In the table view, you can see the overview of the already created processing activities.
Click to enlarge the image
Import processing activity
- In the main menu click on Data protection: A dropdown menu opens.
- In the dropdown menu click on List of processing activities: The table view opens.
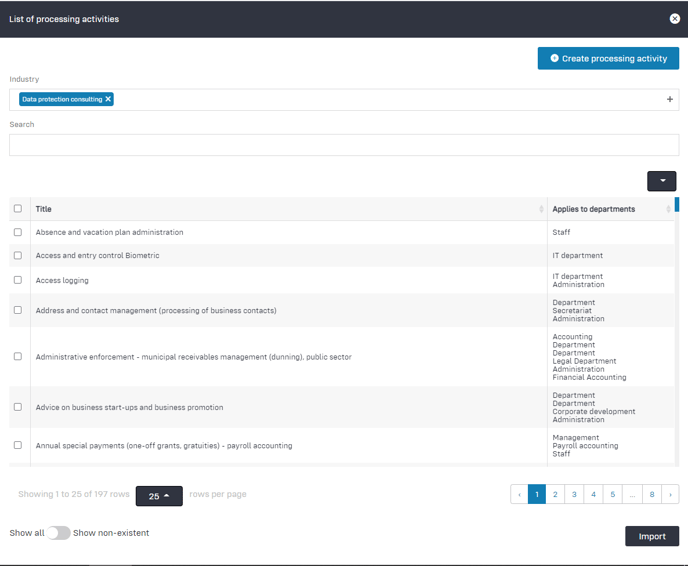
- In the table view click on the button +Processing activity: A slider opens through which the processing activities can be imported from the data base.
Click to enlarge the image
The slider has the following data areas:
- Industry: Select the industry that applies to your company from more than 350 industries.
- Search: Use the search function to look for processing activities from your company.
- Table:
- Checkboxes: In the table, you will find a checkbox in the first column that allows you to select processing activities.
- Title: In the column "Title" you will find the processing activities.
- Applies to departments: The last column on the right shows you in which area the processing activity applies.
- Rows per page: Set how many rows you want to be displayed per page. The default setting is 25 lines per page.
- Pagination: Switch between the different pages.
- Show all /Show non-existent: In so far as you have already imported processing activities, you can hide the already imported processing activities from the table by clicking the button to the right on "Show non-existent".
- Import: By clicking on "Import", the processing activities selected via the checkboxes in the table are transferred to your data protection documentation.
- Close: The slider can be closed by clicking on the "x" Symbol in the top right corner.
- Create processing activity: This function is explained in the next section Create processing activity.
You are a client of Robin Data and are missing a processing activity in your database?
Robin Data will generate missing processing activities for clients upon request. In this case, please contact us via support@robin-data.io and briefly describe the missing processing activity.
Create processing activity
- In the main menu click on Data protection: A dropdown menu opens.
- In the dropdown menu click on List of processing activities: The table view opens.
- In the table view click on the button +Processing activity: A slider opens.
- In the slider click on the button Create processing activity: A quick start input mask opens in which the title can be recorded.
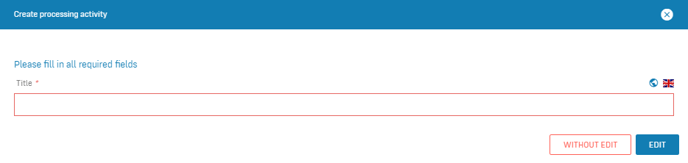
- Fill out the fields of the quick start input mask.
- Click on Edit: An empty input mask opens. For more information on working with input masks, see the article Use input masks with forms.
- Fill out the fields in the input mask.
- Click on Save: The processing activity has been created.
Note
If you select Save without editing in the quick start window, the processing activity will be saved in the table view without any further details, and can be edited at a later time.
Data areas of the input mask
Click to enlarge the image
The left form area has the following data areas:
- Document ID: Assign a document ID to the processing activity, the use of document IDs serves to uniquely mark and identify documents system-wide. Once the ID is stored, it is unchangeable. The letter/number combinations used are based on the specifications of the documented quality management information. These are composed of: Customer name, abbreviation of the selected documented information (Organisational data > Basic data > Information classifications), user e-mail, and the time the ID was generated (date, time, seconds, milliseconds). More information on the help page "Information classifications".
- Specification: Edit the title, description, and organisational controller of the processing activity.
- Legal basis: Define the purpose of the processing activity, its legal basis and justify your own interests in using this process.
- Data subject: Record which data are collected by whom and analyse where the data from this processing activity flows.
- Risk assessment: Assess the risk of the data processing for the data subjects according to a checklist.
- Technical-organisational measure: This data has been transferred to the matcher tab, where it can be selected from the drop-down menu.
Note
The form fields of the data area "Recipient" have been added to the data area "Data subject".
Data area: Specification
This data area has the following form fields:
- Title: Provide a short title (e.g., application intake, social media activities) indicating which processing activity you are documenting.
- Description: Give a compact description of how the procedure (e.g., the receipt of applications) is carried out in your organisation. This description should describe the sub-steps of the process on which the procedure is based.
- Locations: Open the governance tab in the right pane of the input mask and indicate at which locations of the organisation this processing activity applies. One or more locations may be specified. This is a location you have already created or have yet to create under Organisational Data > Organisation > Locations (See article Manage locations).
- Functional area: Open the governance tab in the right pane of the input mask and indicate in which department (e.g., departments or divisions) of the above locations this processing activity applies. This is a functional area you have already created or have yet to create under Organisational Data > Organisation > Functional area (See article Define functional areas).
- Controller: Open the governance tab in the right pane of the input mask and enter the controller (process owner) of the processing activity. This is a person you have already identified or have yet to identify under Organisational data > Organisation > Persons (See article Manage persons help page).
Data area: Legal basis
This data area has the following form fields:
- Purpose of processing: Indicate the purpose for which the process is operated. According to Art. 5 (1)(c) GDPR, the purpose must be adequate and relevant, and limited to what is necessary for the purpose of the processing. As a rule of thumb, one could say that purposes that one does not approve of oneself are not suitable to justify a processing of personal data.
- Legal basis in data protection law: Indicate the data protection-related legal basis of the processing. In addition to federal data protection laws (GDPR, BDSG), specific data protection laws of the federal states as well as of the Catholic and Protestant churches and other religious organisations may apply here. According to 140 GG, recognised religious communities have the option of enacting their own data protection laws or data protection regulations. Article 91 of the GDPR confirms this fact.
- Special legal bases: If the data processing of the processing activity is based on Article 6 (1) (c) of the GDPR (a legal obligation, e.g., transfer of wage data to the tax office) and Article 6 (1) (e) of the GDPR (a task in the public interest or in the exercise of official authority, e.g., food inspections by appointed inspectors), the specific legal bases applied should be specified here. These are very diverse according to the sector of the organisation.
- Consideration of the right to object: Document the consideration of the right to object according to Art. 21 GDPR.
If you are missing a legal basis, we would be happy to receive an e-mail to: support@robin-data.io.
Data area: Data subject
This data area has the following form fields:
- Data subjects: Indicate the data subjects whose personal data are processed in this processing activity.
- Types of data: Enter the data types used in this process. Data types summarise categories of data and are usually concrete documents such as: testimonials, business letters, etc. Selecting the data type will automatically select the associated data categories.
- Data categories: Enter the categories of personal data (e.g., surname, first name, e-mail address, etc.) that will be processed in this process.
- Internal recipient: Select which internal recipients within your organisations receive and process personal data from this processing activity. If no recipient appears in this list, you must set an appropriate internal recipient under Organisational data > Organisation > Recipient.
- External recipient: Select which external recipients recieve and process personal data from this processing activity.
- Service provision: Specify which external contact service or product is used in this processing activity.
- Assigned contract: Select one or more contracts associated with the processing activity (e.g., order processing contract, service contract). If no contract appears in this list, you must set an appropriate contract under Compliance > Contracts & proofs.
- Processing activity of joint controllers: Enter if this is a process operated by joint controllers according to Art. 26 GDPR.
Note
The following data areas have been moved to the matcher tab and can be edited there and viewed under "Summary":
- External recipient: Select "External Contacts" from the drop-down menu under "Internal Documents" to edit this.
- Service provision: Select "Services" from the drop-down menu under "Internal Documents" to edit this.
- Assigned contract: Select "Contracts" from the drop-down menu under "Internal Documents" to edit this.
Data area: Risk assessment
In this data area, you assess what risks the process poses to data subjects. It may be necessary to create a data protection impact assessment under Data protection > Data protection impact assessment.
As a rule of thumb, a data protection impact assessment is required if at least 2 or more of the following criteria are met. However, each risk assessment is a case-by-case decision made by the controller.
- Automated individual case decisions are implemented: Examples are Schufa or credit decisions at banks.
- Data of vulnerable data subjects are processed: Examples are the processing of children or disabled persons. See also glossary data protection.
- Transmission of personal data outside the EU takes place: Example is the transfer of this data outside a company to unsafe third countries such as China.
- Novel technologies are used: Examples include the use of data mining, big data, or machine learning.
- Scoring, profiling, evaluation of persons is carried out: Examples include evaluating performance data in the workplace or sports, scoring to determine creditworthiness.
- Data stocks of personal data are compared or merged: Examples are profiles in social networks or evaluation of different data sources at the workplace.
- Systematic surveillance of persons is carried out: Examples are camera surveillance of workplaces or GPS tracking of cars or trucks or their drivers.
- Large amounts of personal data are processed: Examples include companies that collect data on a large scale (Post, Google, Facebook) or have many customers (e-commerce retailers).
- Difficulties in exercising the rights of the persons concerned exist: Examples include data processing in different countries with language barriers.
- Sensitive personal data are processed: Examples include processing large amounts of health data (e.g., hospital) or processing financial data in a tax office.
Finally, make an assessment of the risks and determine whether a data protection impact assessment is required for this processing activity:
- Risk assessment: The assessment of risks in this processing activity depends on how the individual criteria have been assessed. It is usually dependent on the context and should ideally be made jointly within the data protection organisation. If at leaste two of the above criteria are met, the risk should be assess as at least medium. If more than two criteria are met, the risk should be assessed as high.
- Data protection impact assessment required: If the risk is assessed as medium, a data protection impact assessment may be required. If the risk is assessed as high, a data protection impact assessment is mandatory. You can perform a data protection impact assessment under Data protection > Data protection impact assessment.
Data area: Technical-organisational measure
- Technical-organisational measure: Use the search or scroll through the list of TOMs to store a corresponding technical-organisational measure. The TOMs are created or imported under Compliance > Technical-organisational measures.
Note
This data area has been moved to the matcher tab and can be edited there and viewed under "Visualisation".
The right form area has the following data areas:
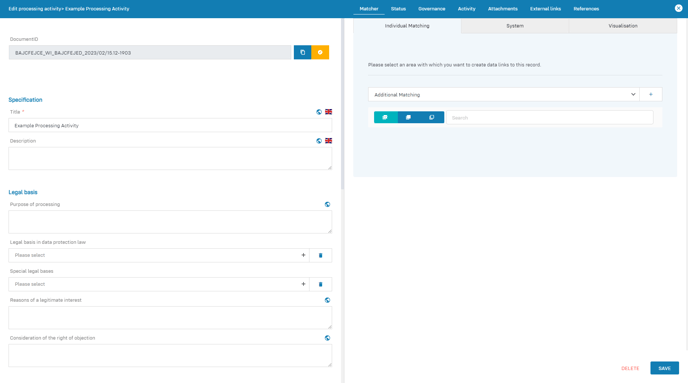
- Matcher Tab: You can use the matcher to link documents (such as activities or technical and organizational measures) and view linked documents. The matcher can be used to create additional documents that can be linked to the open record. For a more detailed explanation, see the article Use the matcher.
- Status Tab: In this tab it is possible to manage the status of a document and to store notes about the erasure class.
- Governance Tab: The Governance Tab is equally available in several documents in the Robin Data software. It offers the possibility to record various basic parameters for the respective document. a more detailed explanation can be found in the article Manage Governance Content.
- Attachments tab: In this tab you can add related documents by clicking the Add Attachment button. For a more detailed explanation, see the article Use input masks with forms.
- External Links Tab: In this tab you can link related information using the Add external link button. For a more detailed explanation, see the article Use input masks with forms.
Note
The functions of the former activities tab and references tab have been added to the matcher tab. Via the matcher, activities and erasure classes can be created and linked to data records.
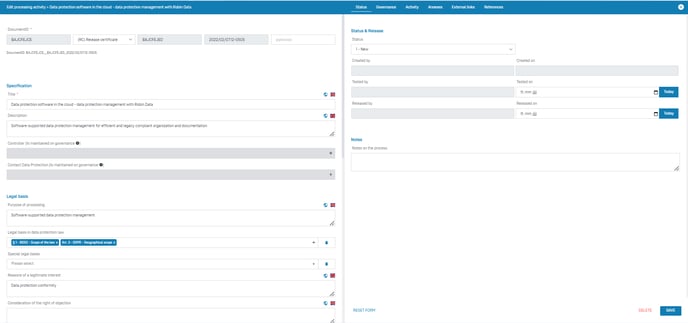
Data area: Status
In this data area it is possible to manage the status of a document and to map the release procedure of the document.
- A processing activity is usually created by one person, for example the employee of a specialist department.
- In addition to this person, another person should check whether the process complies with the law. This can be done by the data protection officer, for example.
- At the end of the chain, someone must officially approve the processing activity. This can be done, for example, by the supervisor.
This data area has the following form fields:
- Status: Indicate the current processing status of the processing activity.
- Created by: Indicate the person who created this processing activity.
- Created on: Enter the date on which the creation of this processing activity was completed.
- Tested by: Enter the person who audited this processing activity.
- Tested on: Enter the date on which the audit of this processing activity was completed.
- Released by: Enter the person who released this processing activity.
- Released on: Enter the date this processing activity was released for use.
- Notes: This field provides space for your notes on this processing activity.
- Color coding of the document: Assign a color code to the document. Color codes are defined via Organisational data > Management system > Content groups.
Edit processing activity
- In the main menu click on Data protection: A dropdown menu opens.
- In the dropdown menu click on List of processing activities: The table view opens.
- In the table view click on the Title column of a processing activity: The processing activity opens.
- Edit the processing activity.
- Click on Save: The changes to the processing activity have been saved.
The different data areas are explained in more detail in the item Create processing activity. In addition, you will find the data areas "Activity" and "Reference" on the right side of the input mask.
Click to enlarge the image
Copy direct links to processing activities
In the processing activities, direct links to the data records can be copied and pasted into an e-mail, for example. After clicking on the link, users get to the corresponding data record. The prerequisite is that users are logged in to Robin Data.
- In the main menu click on Data protection: A dropdown menu opens.
- In the dropdown menu click on List of processing activities: The table view opens.
- In the table view click in the Title column of a processing activity: The processing activity opens.
-
Click on the orange symbol next to the document ID: The link to the processing activity has been saved to your clipboard and can be copied.
Print processing activity
Starting with the "Basic" license, you can print a selection of your processing activities and download it in the form of a PDF.
Tip: Print threshold analysis
The result of the threshold analysis is also printed if you have selected "yes" once for the data area "Perform threshold analysis" and then cancelled this selection. This serves the documentation obligation of the GDPR to be able to prove that the risk of the respective processing activity was checked.
- In the main menu click on Data Protection: A dropdown opens.
- In the dropdown menu select List of Processing Activities: The table view opens.
- Option 1: Click in the first columnn on the checkboxes to select individual processing activities: Selected processing activities are marked with a blue check mark.
- Option 2: Click in the column header of the checkboxes to select all processing activities: Selected processing activities are marked with a blue check mark.
- Click on the button Actions: A dropdown list opens.
- In the dropdown list click on Print: A window opens.
- Click on OK: The processing activities will be downloaded as PDFs.
Click on the image to make it larger.
Related links
- Wiki article Record of processing activities
Further questions? - We are here for you.
If you have any questions about the software, please contact our support team. You can reach us at support@robin-data.io.
-1.png?width=688&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(6)-1.png)